Hyperlipidemia is a condition characterized by elevated levels of lipids in the blood, which can lead to significant health issues if not managed properly. Understanding this condition is critical for healthcare professionals, especially nurses who play a pivotal role in patient care and medication administration. In this article, we will explore hyperlipidemia in-depth, focusing on its causes, consequences, and the importance of cautious medication administration by nurses. Through thorough investigation and reliable sources, we aim to provide valuable insights that enhance the understanding of this condition.
As healthcare providers, nurses must be well-versed in the implications of hyperlipidemia management. This article will cover various aspects of hyperlipidemia, from its definition and risk factors to practical nursing interventions. The cautious administration of medications is crucial, as patients with hyperlipidemia may have unique responses to treatment and potential interactions with other medications they are taking.
By the end of this article, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of hyperlipidemia, its impact on patient health, and the critical role of nurses in ensuring safe and effective treatment. Let's delve into the details of this condition, exploring what makes cautious administration a necessity.
Table of Contents
Definition of Hyperlipidemia
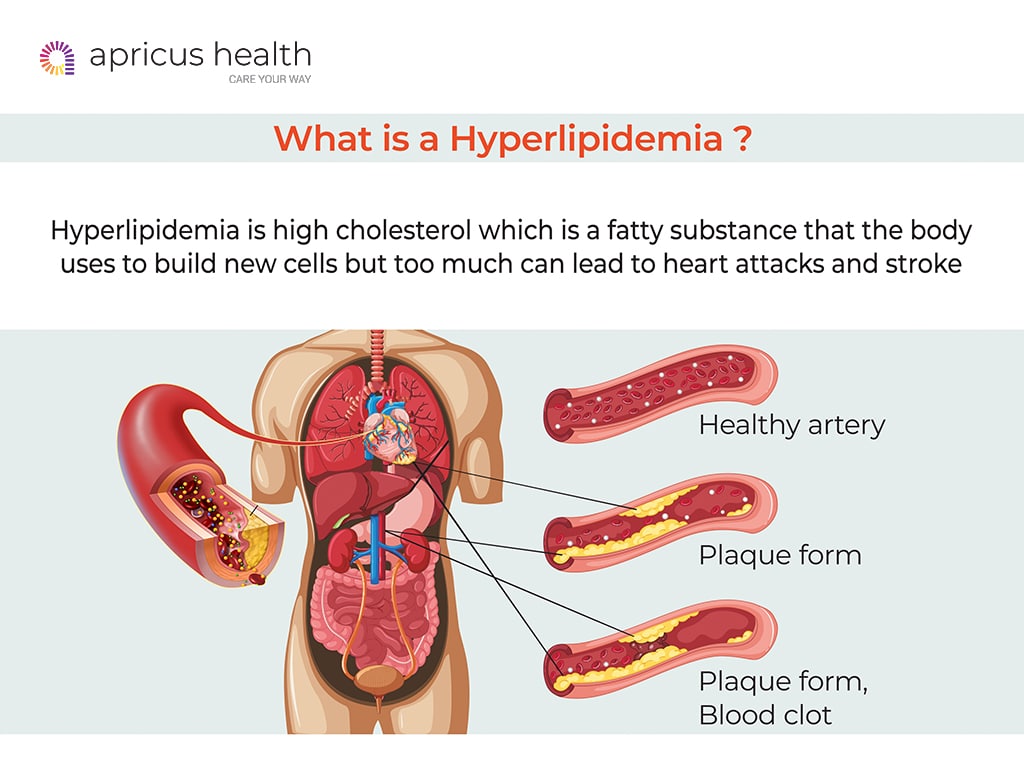
Hyperlipidemia refers to an abnormal elevation of lipids in the bloodstream, including cholesterol and triglycerides. These lipids are essential for various bodily functions, including hormone production and cellular repair, but excessive levels can lead to serious health issues, including cardiovascular diseases.
Causes of Hyperlipidemia
The causes of hyperlipidemia can be classified into two main categories: primary and secondary causes.
Primary Causes
These are genetic disorders that affect lipid metabolism. Common primary causes include:
- Familial hypercholesterolemia
- Familial combined hyperlipidemia
Secondary Causes
Secondary causes are often related to lifestyle and other medical conditions. They include:
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypothyroidism
- Certain medications (e.g., diuretics, beta-blockers)
Risk Factors Associated with Hyperlipidemia
Several risk factors contribute to the development of hyperlipidemia, including:
- Age and gender (men are at higher risk earlier in life)
- Family history of hyperlipidemia or cardiovascular diseases
- Unhealthy diet high in saturated fats and trans fats
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
Symptoms of Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia often presents no symptoms, which is why it is known as a "silent" condition. However, severe cases can lead to symptoms associated with complications, such as:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Heart attack
- Stroke
Diagnosis of Hyperlipidemia
Diagnosis is typically made through blood tests that measure lipid levels. Key tests include:
- Lipid panel (measuring total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides)
- Fasting blood glucose test (to check for diabetes)
Treatment Options
Treatment for hyperlipidemia may involve lifestyle changes, medications, or both. Common treatment options include:
- Dietary modifications (reducing saturated fat and increasing fiber intake)
- Regular physical activity
- Medications such as statins, fibrates, and niacin
Nursing Care for Hyperlipidemia
Nurses play a crucial role in managing patients with hyperlipidemia. Their responsibilities include:
- Monitoring lipid levels and overall health
- Educating patients about lifestyle changes
- Administering medications cautiously and monitoring for side effects
Conclusion
In conclusion, hyperlipidemia is a significant health concern that requires careful management. Nurses must be proactive in assessing, educating, and administering treatments to ensure patient safety. Understanding the complexities of hyperlipidemia allows healthcare providers to offer the best care possible.
We encourage readers to leave comments or share their thoughts on this article. Your feedback is invaluable as we strive to provide informative content. For more articles on health and wellness, please explore our site further.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you again soon!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8qcXPnqmloaCesaa5yJpkraCVYru2vtKeZJ2dpJq%2FrrXNnqpmm5Gqwaq71Kxkmpydnruqv9OrmK2hn6N6qr%2BMsJirqpGjwaawjaGrpqQ%3D