Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a complex mental health condition that can arise following the death of a client, particularly for professionals in caregiving roles. This condition can manifest in various ways, affecting not just the emotional well-being of the individual but also their professional efficacy and personal life. Understanding the implications of PTSD in such contexts is crucial for mental health professionals, caregivers, and anyone working closely with individuals who experience traumatic events.
In this article, we will delve into the nuances of PTSD, specifically focusing on how it can develop after the death of a client. We will explore the signs and symptoms, the psychological impact, coping mechanisms, and effective treatment options available. Our aim is to provide a comprehensive guide that not only informs but also supports those who are affected by this condition.
Throughout the article, we will reference credible sources and provide actionable insights to foster understanding and recovery. Whether you are a mental health professional, a caregiver, or someone seeking to understand PTSD better, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate this challenging terrain.
Table of Contents
What is PTSD?
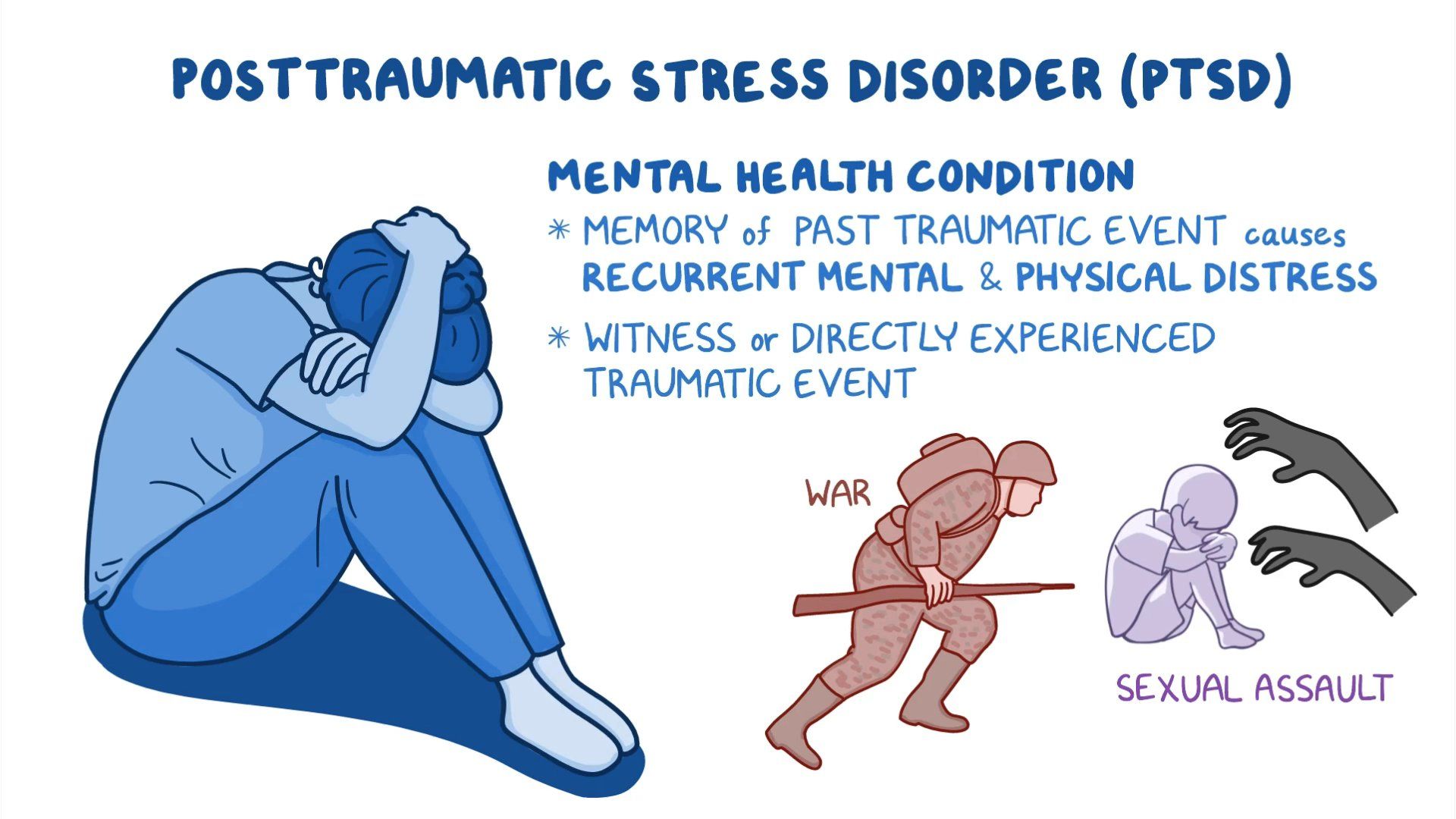
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health disorder that can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. While commonly associated with military veterans, PTSD can affect anyone who has faced a traumatic experience, including the death of a client in a professional setting. The symptoms of PTSD can vary widely, but they typically include intrusive thoughts, avoidance behaviors, negative changes in mood and cognition, and heightened arousal responses.
Key Characteristics of PTSD
- Re-experiencing the trauma through flashbacks or nightmares.
- Avoidance of reminders related to the trauma.
- Negative changes in mood and thinking.
- Increased arousal symptoms, such as irritability or hypervigilance.
Causes of PTSD After Client Death
The death of a client can trigger PTSD for various reasons. Professionals may feel a strong sense of loss or guilt, especially if they believe they could have done more to prevent the death. Factors that contribute to the development of PTSD in these situations include:
- Nature of the relationship with the client.
- Suddenness or unexpectedness of the death.
- Previous experiences with trauma.
- Support received from colleagues or supervisors.
Signs and Symptoms of PTSD
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of PTSD is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Flashbacks or intrusive memories of the client's death.
- Difficulty sleeping or insomnia.
- Emotional numbness or detachment.
- Heightened anxiety or panic attacks.
Emotional and Physical Symptoms
PTSD symptoms can manifest both emotionally and physically. Emotional symptoms include persistent sadness, anger, or irritability. Physical symptoms may involve fatigue, headaches, or gastrointestinal issues. Understanding these manifestations can aid in recognizing when help is needed.
Impact of PTSD on Professionals
The impact of PTSD on professionals who experience the death of a client can be profound. It can affect their work performance, relationships, and overall quality of life. Common effects include:
- Increased absenteeism from work.
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions.
- Strain in personal relationships.
- Potential for burnout and job dissatisfaction.
Coping Mechanisms for PTSD
Coping with PTSD after the death of a client requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some effective coping mechanisms:
- Engaging in regular physical activity to reduce stress.
- Practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques.
- Maintaining a strong support network of friends and colleagues.
- Seeking professional help and counseling.
Treatment Options for PTSD
There are several evidence-based treatment options for PTSD that can help individuals recover:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Focuses on changing negative thought patterns.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): Helps process and integrate traumatic memories.
- Medication: Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed.
- Support groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide comfort.
The Importance of Support Systems
Having a robust support system is vital for those experiencing PTSD. Support can come from various sources:
- Friends and family: Providing emotional support and understanding.
- Colleagues: Sharing experiences and coping strategies.
- Professional organizations: Offering resources and training.
- Mental health professionals: Providing therapy and guidance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) after the death of a client is essential for both professionals and caregivers. Recognizing the signs, seeking treatment, and fostering strong support systems can significantly impact recovery. If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD, it is important to take action and seek help. Together, we can create a supportive environment for healing and growth.
We encourage you to leave your thoughts in the comments below, share this article with others who may benefit from it, or explore more of our articles on mental health topics.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again on our site for more insightful content!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8uLXToWSpp6OpwbOt1KaYraGTYsC1vsSsqmacmai8s7DEq2SprKOZeqKy056pZqyYmnqlscCtn2anlmLBqbGMnKOinZ6pwG%2B006aj