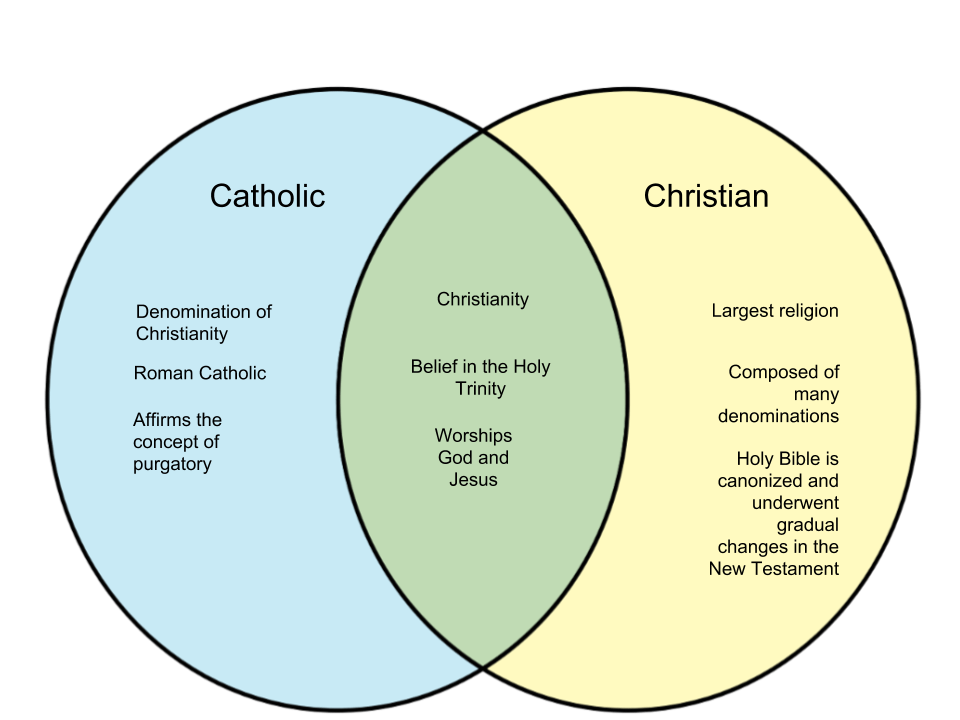
The debate between Catholicism and Christianity has been a topic of interest for many individuals seeking to understand the nuances of faith. Catholicism is often seen as a branch of Christianity, but it holds distinctive beliefs and practices that set it apart. In this article, we will explore the key differences and similarities between Catholicism and Christianity, providing an insightful perspective on this important topic.
The terms "Catholic" and "Christian" are often used interchangeably, creating confusion for those unfamiliar with their meanings. While all Catholics are Christians, not all Christians are Catholics. This article aims to clarify these terms, delve into their historical backgrounds, and examine their theological differences. By the end of this discussion, readers will have a deeper understanding of these two expressions of faith.
Understanding the distinctions between Catholicism and Christianity is essential for fostering dialogue and respect among different denominations. With millions of followers worldwide, both groups contribute significantly to the global religious landscape. Let’s embark on this journey to explore the rich tapestry of beliefs that define Catholics and Christians.
Table of Contents
1. Defining Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. It encompasses a wide range of beliefs and practices, with various denominations interpreting the Bible differently. The core belief of Christianity is the conviction that Jesus is the Son of God and the Savior of humanity. Christians believe in the Trinity, which consists of God the Father, God the Son, and God the Holy Spirit.
Christianity began in the 1st century AD in the Roman province of Judea and has evolved over the centuries into numerous denominations, including Protestantism, Orthodoxy, and Catholicism. Each denomination has unique interpretations of scripture and varying practices of worship.
2. What is Catholicism?
Catholicism is the largest Christian denomination, with over a billion adherents worldwide. It is characterized by its adherence to the authority of the Pope, who is considered the spiritual leader of the Catholic Church. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the one true church founded by Jesus Christ, and it claims to possess the fullness of the means of salvation.
Distinctive features of Catholicism include the sacraments, the veneration of saints, and the significance of tradition alongside scripture. The Catholic Church emphasizes the importance of community and the sacraments as a means of grace.
Data and Personal Information
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1st Century AD |
| Number of Followers | Over 1 billion |
| Headquarters | Vatican City |
| Key Figure | Pope |
3. Historical Context of Catholicism and Christianity
The history of Christianity and Catholicism is deeply intertwined. After the death of Jesus, his followers began to spread his teachings, leading to the establishment of early Christian communities. The first major split in Christianity occurred in 1054 AD, known as the Great Schism, which divided Christians into Eastern Orthodox and Western Catholic branches.
The Protestant Reformation in the 16th century marked another significant division within Christianity. Reformers like Martin Luther challenged the practices of the Catholic Church, leading to the emergence of various Protestant denominations. This historical context is crucial for understanding the differences and similarities between Catholic and Protestant Christians today.
4. Key Differences Between Catholics and Christians
While all Catholics are Christians, there are several key differences that distinguish Catholic beliefs from those of other Christian denominations:
- Papal Authority: Catholics recognize the Pope as the ultimate authority, whereas many Protestant denominations reject papal authority.
- Sacraments: Catholics observe seven sacraments, while Protestant denominations may only recognize two (baptism and communion).
- Tradition: Catholicism places a strong emphasis on tradition alongside scripture, while many Protestant Christians prioritize scripture alone (sola scriptura).
- Veneration of Saints: Catholics venerate saints and seek their intercession, a practice not commonly found in Protestantism.
5. Similarities Between Catholics and Christians
Despite their differences, there are several fundamental similarities between Catholics and other Christians:
- Belief in Jesus Christ: Both Catholics and Christians believe in Jesus Christ as the Son of God and the Savior.
- Scripture: Both groups hold the Bible as sacred scripture, although the canon may differ slightly.
- Faith and Grace: Both emphasize the importance of faith and grace for salvation.
- Community Worship: Both participate in communal worship and celebrate the significance of gathering together.
6. The Role of the Bible in Both Faiths
The Bible plays a central role in both Catholicism and Christianity, serving as the primary source of religious teachings and moral guidance. However, their approaches to scripture differ:
- Catholic Bible: The Catholic Church includes the Deuterocanonical books in its canon, resulting in a total of 73 books.
- Protestant Bible: Many Protestant denominations adhere to a 66-book canon, omitting the Deuterocanonical books.
7. Catholic Sacraments vs. Christian Practices
Catholicism is known for its sacraments, which are seen as vital means of grace. The seven sacraments include:
- Baptism
- Confirmation
- Eucharist (Communion)
- Confession (Reconciliation)
- Marriage
- Holy Orders
- Anointing of the Sick
In contrast, most Protestant denominations typically recognize only baptism and communion as sacraments or ordinances, with varying beliefs about their significance.
8. The Future of Catholicism and Christianity
As society continues to evolve, both Catholicism and Christianity face new challenges and opportunities. The rise of secularism and interfaith dialogue presents unique contexts for both groups to reevaluate their beliefs and practices. Cooperation in social justice initiatives and addressing global issues such as poverty and climate change may foster a greater understanding between Catholics and other Christians.
In conclusion, the distinctions and commonalities between Catholicism and Christianity highlight the richness of the Christian faith. Understanding these differences fosters respect and dialogue among various denominations. We encourage readers to reflect on their beliefs and engage in conversations about faith with openness and curiosity.
We invite you to leave a comment below, share this article with others, or explore more content on our site to deepen your understanding of religious beliefs.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you again soon!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmmqaUpH53e8Kaq6GnnJ6wbsLSZpqhqpmowaqtzWefraWc