Replication bubbles are crucial mechanisms in DNA replication, playing a significant role in the process of cell division and genetic inheritance. This article dives deep into the concept of replication bubbles, their formation, and their importance in the biological sciences. By the end of this exploration, you will have a comprehensive understanding of replication bubbles and their implications in genetics.
In this discussion, we will analyze various aspects of replication bubbles, including their structure, function, and the factors that influence their dynamics. Additionally, we will address common questions and misconceptions regarding this fundamental biological concept. Whether you are a student, researcher, or simply curious about molecular biology, this article aims to provide valuable insights.
So, let's embark on this journey to demystify replication bubbles and discover how they fit into the larger context of DNA replication and cell biology.
Table of Contents
What are Replication Bubbles?
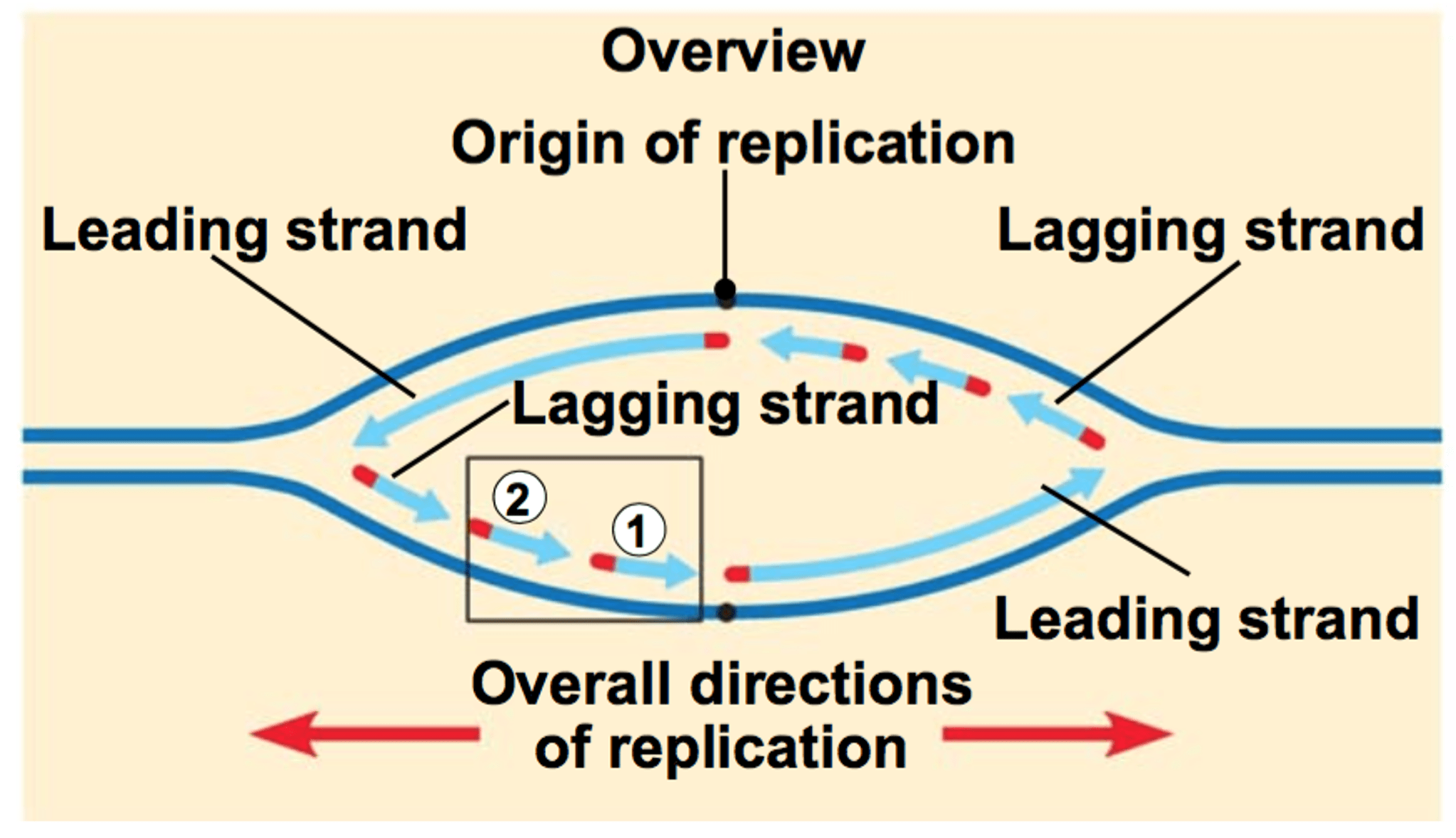
Replication bubbles are regions of DNA where the double helix unwinds, allowing for the synthesis of new DNA strands. They form during the initiation phase of DNA replication, which is essential for the accurate duplication of genetic material.
Structure of Replication Bubbles
Each replication bubble consists of two replication forks that move away from each other, effectively creating a "bubble" in the DNA strand. This structure is vital for the replication process, as it allows for bidirectional synthesis of DNA.
Formation of Replication Bubbles
The formation of replication bubbles begins at specific locations on the DNA molecule known as origins of replication. These sites are recognized by various proteins that facilitate the unwinding of the DNA strand.
Mechanism of Formation
The steps involved in the formation of replication bubbles include:
- Recognition of the origin of replication.
- Binding of initiator proteins.
- Unwinding of the DNA double helix.
- Formation of the replication fork.
Function of Replication Bubbles
The primary function of replication bubbles is to allow for the efficient and accurate replication of DNA. This is crucial for cell division and the maintenance of genetic integrity.
Role in DNA Replication
Replication bubbles facilitate the following:
- Simultaneous synthesis of new DNA strands.
- Reduction of replication errors.
- Coordination of various enzymes involved in DNA synthesis.
Factors Influencing Replication Bubbles
Several factors can influence the dynamics and stability of replication bubbles, including:
- Environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, pH).
- Presence of specific proteins and enzymes.
- DNA sequence variations.
Common Misconceptions about Replication Bubbles
Despite their importance, there are several misconceptions surrounding replication bubbles:
- They only occur in eukaryotic cells.
- Replication bubbles are static structures.
- All DNA replication occurs in a single direction.
Importance of Replication Bubbles in Genetics
Replication bubbles play a critical role in genetics, particularly in how genetic information is passed from one generation to the next. Errors in replication can lead to mutations, which can have significant implications for health and disease.
Current Research and Studies
Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into the mechanisms of replication bubbles. Recent studies have focused on the implications of replication errors and how they contribute to genetic disorders and cancer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, replication bubbles are essential components of DNA replication, facilitating the accurate duplication of genetic material. Understanding their formation, function, and influence is crucial for advancing our knowledge in molecular biology and genetics. If you have any questions or thoughts about replication bubbles, feel free to leave a comment below. Don’t forget to share this article and explore more content on our site!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you again soon!
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7rLHLpbCmp5%2Bnsm%2BvzqZmm6efqMFuxc6uqWarlaR8o63Snptmp55iwamxjJ%2BmpaSfrLavs4yrnKmkmZiutbXOp2SbrZKXuaZ51qGgnKBdpLNuwMeeZJ%2BnnKG8uLXNoGWhrJ2h